OCSP
From version: 1.8.0
Certdog can provide OCSP services for local CAs and external CAs (e.g. Microsoft AD CS)
When using OCSP services for local CAs, certdog can setup all of the components required to enable automatic issuance of an OCSP signing certificate, and retrieval of the certificate status. Users just need to select the Create OCSP Server option when creating (or editing) a Local CA
When using OCSP services for external CAs, users must create the OCSP configuration manually
Configuration for an Internal CA
From the Local CA (Local CAs, CA Configuration menu), simply check the Create OCSP Server option:
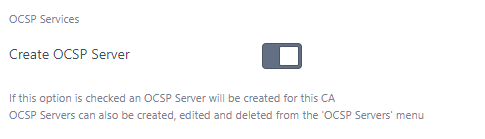
Once Add (or Update) is clicked for the Local CA, the following will then be automatically generated:
- An OCSP Server. You can view configured servers from the OCSP Servers menu item
- A Certificate Profile. This profile will be configured to issue OCSP signing certificates
- A Certificate Issuer. This will combine the profile above with the local CA - so that the CA is able to issue OCSP signing certificates
- A User and a Team. The user will be a member of the team and the team will only have permissions to request certificates from the Certificate Issuer mentioned above. The user account will be used by the OCSP server to authenticate to certdog and request a signing certificate
With the above items in place an OCSP server will automatically obtain a signing certificate from the CA. This certificate will also be auto-renewed
Certificate status will be obtained from the internal database meaning this information will be up to date
You may edit the OCSP settings my clicking on the OCSP Servers menu then selecting the OCSP server (see OCSP Server Settings for the specific settings)
Configuration for an External CA
For external CAs (e.g. a Microsoft AD CS instance) an OCSP server must be manually created. to do this from the OCSP Servers menu, click Add New OCSP Server then complete following the OCSP Server Settings section below
OCSP Server Settings
The following settings are available for each OCSP Server
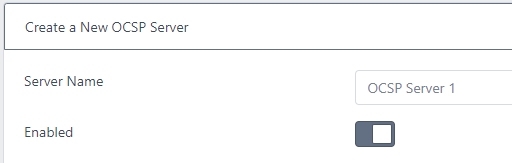
- Server Name
- This is simply the OCSP Server name. It can be changed without affecting any functionality
- Enabled
- If not enabled the OCSP server will not process any OCSP requests. Unauthorized will be returned
Status Source Location
This is where the information about the certificate status (good or revoked) will be obtained. Options are to retrieve from the internal database (for local CAs) or from CRL files
This can be set to one of the following
Local CA (database)
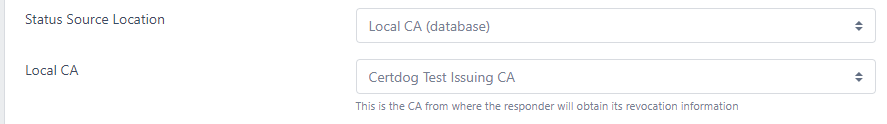
The status will be obtained from the internal database of a local CA. This will provide the most up to date certificate status information
If you select this option then the Local CA option will be available
-
Local CA
Select the local CA from the drop down list
Local CRL File
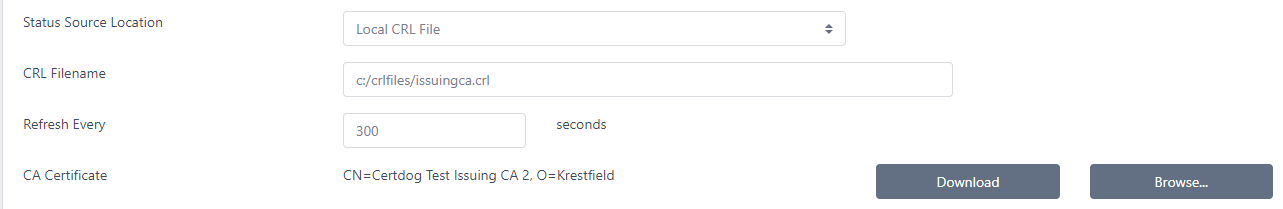
Obtain status from a local CRL file
If you choose this option you must then set the following options
-
CRL Filename
The full path to the CRL file. The file that must be located on the server hosting certdog (not your local machine)
-
Refresh Every
The period at which to re-read the file to get up to date information. Note, the OCSP server will also automatically re-read the CRL when it expires
-
CA Certificate
The certificate of the CA that this OCSP server is providing information for
Click Browse.. to navigate to this certificate. This file can be uploaded from your local machine and does not need to reside on the certdog server
CRL URL
Obtain status from a CRL hosted at an http address
If you choose this option you must then set the following options
-
CRL URL
The http location of the CRL e.g. http://server.certdog.local/crl/issuingca.crl of the CRL
-
Refresh Every
The period at which to re-read the file to get up to date information. Note, the OCSP server will also automatically re-read the CRL when it expires
-
CA Certificate
The certificate of the CA that this OCSP server is providing information for
Click Browse.. to navigate to this certificate. This file can be uploaded from your local machine and does not need to reside on the certdog server
Signing Certificate Renewal Details
This section contains details about the OCSP signing certificate, including where to obtain it from, what to name it and when to renew
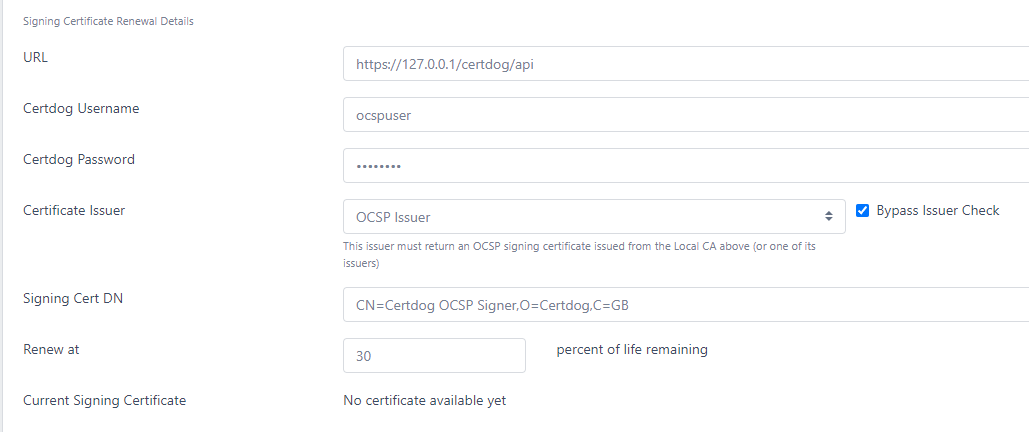
- URL
- This is the Certdog API URL that the OCSP server will use to request certificates. It will be of the form
https://[certdog server]/certdog/api - See Operational Notes below for details as to why this is required
- Note: If running on a Linux machine or other where you are mapping external ports to internal ones, ensure you correct the URL. For example, if your local services are listening on port 1433 (routed from external port 443), the internal address should be https://127.0.0.1:1433/certdog/api rather than https://127.0.0.1/certdog/api
- This is the Certdog API URL that the OCSP server will use to request certificates. It will be of the form
-
Certdog Username
- This is the username of the account that has permissions to request the OCSP signing certificate. If the OCSP was created automatically, this user account would have been generated for you. If you wish to configure this yourself, use an account that has permissions on the Certificate Issuer which will provide the correct OCSP Signing certificates
-
Certdog Password
- This is the password associated with the account name mentioned above
-
Certificate Issuer
- This is the Certificate Issuer. If the OCSP was created automatically, this issuer would have been generated for you. If you wish to create this yourself, the issuer must be associated with the same CA that this responder is serving and be configured with an OCSP compliant Certificate Profile (See OCSP Certificate Profile below)
- Bypass Issuer Check
- If setting manually for an external CA (not a Local CA hosted by certdog), select this option
- By default the Certificate Issuer must be associated with the same CA as the Local CA i.e. you obtain an OCSP signing certificate from the CA whose status is being provided by the OCSP server. In some cases you may want to issue an OCSP signing certificate from another CA or the root CA. If this option is checked it will then allow these configurations
-
Signing Cert DN
- If you wish for the OCSP Signing certificate to have a specific DN, you may set it here. If this is left empty a default DN will be created of the form:
CN=OCSPServer-[CA Name]-[ID]
- If you wish for the OCSP Signing certificate to have a specific DN, you may set it here. If this is left empty a default DN will be created of the form:
- Renew at
- This is the percentage of life remaining on the OCSP Signing certificate at which it will be renewed. For example, if you set this to 50. When the current signing cert has 50% of its lifetime remaining, it will be renewed.
-
Current Signing Certificate
- This provides a link to the current OCSP signing certificate in use. If no certificate has been issued (e.g. when initially setting up) this will show No certificate available yet
- Renew Certificate
- This option is only visible once a certificate has been issued
- If this option is checked, the current OCSP signing certificate will be renewed at the next expiry check (which by default is every minute) whether it is currently expiring or not. Check this option if you have made changes to the certificate details such as Certificate Issuer or Signing Cert DN and wish to force a renewal
Key Store and Signing Algorithm Details
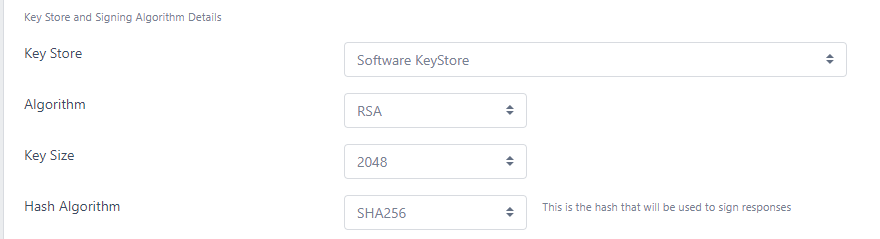
- Key Store
- This is the Key Store where the responder will store its own signing keys. By default the same Key Store as used by the CA is selected, but another can be configured
- Algorithm
- The algorithm that will be used to sign OCSP responses (this also dictates what algorithm the signing certificate will use)
- Key Size
- The key size of the signing certificate if RSA is selected as the Algorithm
- Curve
- The ECC curve. If ECDSA is selected as the Algorithm
- Hash Algorithm
- This is the hash algorithm that will be used when signing OCSP responses and not the algorithm that will be included in the signing certificate (as this is dictated by the issuing CA). Some systems require a specific hashing algorithm to be configured
Other Settings
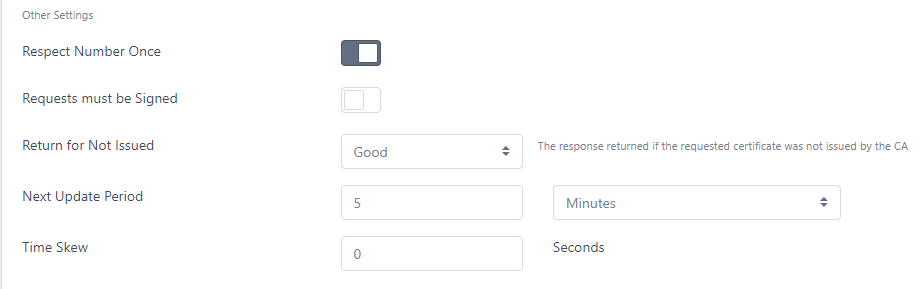
- Respect Number Once
- If this is checked, if a Number Once value is provided in the OCSP request, that same value will be returned in the response. This option is often employed by clients to ensure that the OCSP response is freshly generated
- Requests must be signed
- If this option is checked then OCSP requests must be signed and will be rejected (with an Unauthorized response) otherwise
- Return for Not Issued
- If an OCSP request is received for this CA but the serial number of the certificate has not been issued from this CA, here you can specify what to return in this instance.
- If the OCSP responder is being used to provide responses for an external CA (such as Microsoft), it is unable to verify all issued serial numbers, so this option should be set to Good
- For internal CAs, this should be set to either Revoked or Unknown, depending on how your clients will cope with those responses e.g. if your clients will continue even if the response is Unknown, you may need to set the response to Revoke to force the client to reject the response
- Note that CAB Forum, compliance 2013-08-01 section 3.2.2.6 states OCSP Responders SHALL NOT respond “Good” for Unissued Certificates. Therefore, if you need to adhere to this requirement, ensure that Good is not set
- Next Update Period
- This is the time that will be added to the Produced At period of the OCSP response, and is essentially the validity of the response
- Time Skew
- If there are any clock deviations between clients and the OCSP Server, you may set this value to allow a time skew (in seconds). E.g. if you set this value to 5 then the produced at date of the OCSP response will be NOW minus 5 seconds and the response’s expiry date (Next Update) will be EXPIRY TIME plus 5 seconds
Operational Notes
Although they run on the same server by default, OCSP Servers run independently of certdog. This is to allow for the OCSP Server to run on a separate machine to the certdog instances. E.g. you may wish to run your OCSP servers in a more accessible environment and load-balance
It is for this reason that the certdog URL, Username and Password need to be set above - as the certdog instance providing the certificates may not always be on the same machine
OCSP End Point (AIA)
By default the OCSP server will be located at the following URL
http://[server name]/certdog/ocsp
For example, if your certdog server is at https://certdog.krestfield.com then your OCSP end point would be
http://certdog.krestfield.com/certdog/ocsp
Note: The URL is not SSL protected (http rather than https). This is intentional as SSL protected OCSP end points are not often utilised (and not supported by many systems)
If you do require an SSL protected end point, contact krestfield support
You may have additional DNS settings that reference the certdog server e.g.
CNAME: status.pki.com -> certdog.krestfield.com
Which would mean your OCSP services could be contacted at:
http://status.pki.com/certdog/ocsp
Whatever location/URL you choose, this value must be added as the AIA OCSP Location for certificates issued from the CA. This value will be populated for you when you select the Create OCSP Server option for a Local CA, but if using an external CA this value must be set there
OCSP Certificate Profile
If you wish to create your own Certificate Profile for an OCSP server you must configure the following:
- Key Usage
- This must include the digital signature key usage
- Enhanced Key Usage
- This must include the OCSP Signing option
Optionally, you may set Include OCSP No Check. This indicates to the client that the OCSP signing certificate itself should not be OCSP checked. If this is not set, then the client may then carry out an additional OCSP check on the OCSP signing certificate itself