Certdog Architecture
The certdog application is made up of the following main components:
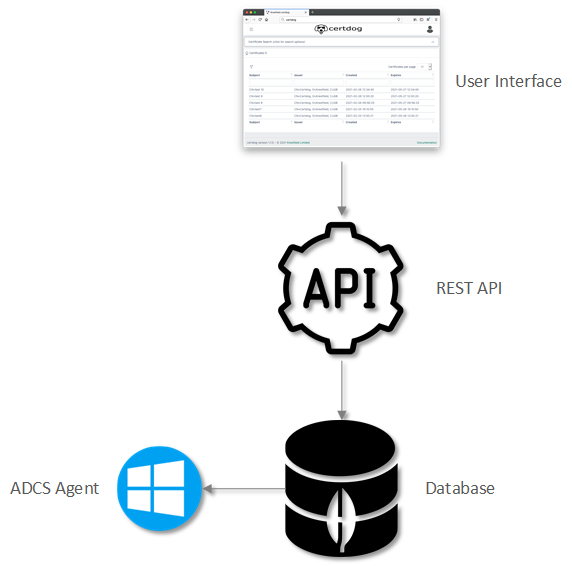
The User Interface
A web based front end that allows for system configuration and the management of certificates (requesting, searching, revoking etc.)
It allows users and administrators to login and perform operations. Available operations are dependant on what privileges the logged in user has e.g. a standard user will not have any administrative (e.g. user management) operations available
The UI performs very little processing. All operations are handed off to the API making it a lightweight component. This this also means that everything that you can do via the UI can be done via the REST API
The REST API
This is available to all users who have a valid logon. That is, if they can authenticate to the UI they can make use of the REST API
Available operations can be viewed using the Swagger interface that can be accessed at this location:
https://[servername]/certdog/api/swagger-ui.html
E.g.
https://127.0.0.1/certdog/api/swagger-ui.html
If you wish to develop your own applications that make use of certdog features, you should develop against this API
The Database
Certdog uses a mongo database which offers speed and flexibility. For example, you may host your database locally (the default), on a separate server or in the cloud (MongoDB Atlas)
You can use a dedicated instance or use an existing instance you already have in place
If any other components are updated, there is usually no need to also update the database
There are several simple mechanisms for backing up the data
Sensitive data stored in the database is encrypted by the API service before being stored
The ADCS Agent
This is the component that interfaces with the Microsoft CA (Active Directory Certificate Services)
It communicates directly with the database to increase performance. This means that as soon as a request is placed, the database can push the request to the agent for immediate processing. The alternative would be to continually poll the API for requests, which would create additional overhead (due to the continual polling) and delays from requesting a certificate to it being returned
By default all communication between the components is protected via TLS