ACME
This feature is available from certdog 1.16
Certdog supports the ACME protocol (RFC8555) including External Account Binding (EAB)
Multiple ACME end points can be created - each with a different configuration. This allows for multiple setups that may provide different certificate types from different CAs
Configuration
From the menu, select Interfaces and then choose ACME
Click Add New ACME Service:
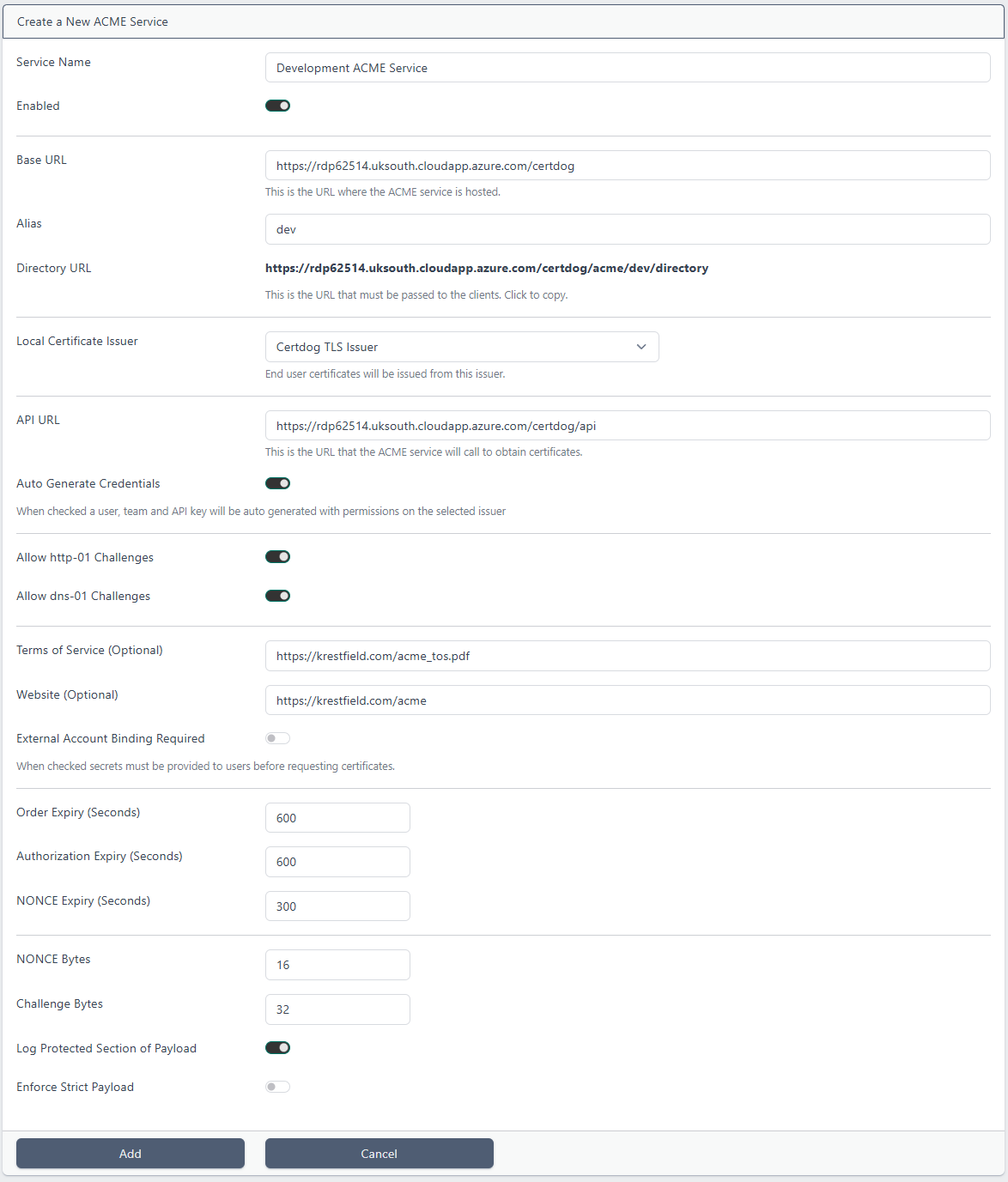
- Service Name. Enter a name. This can be anything to identify the service to the administrators. End users will not see this value
- Enabled. This enables the service. If this is un-checked clients will receive an error indicating that the service is disabled
- Base URL. This will be pre-populated using the servers System URL. If that value has not been set or you need to alter this value (e.g. if the URL that clients will access uses a DNS address or goes via some load-balancer etc.), then update it here
- Alias. This is what will define the specific Directory URL for this service, that clients will initially target. It is simply appended to the URL to make it unique. It should not contain spaces
- Directory URL. This is value will be calculated from the Base URL and Alias. This is the value should be provided to clients
- Local Certificate Issuer. Choose from the drop down, the issuer from where certificates targeting this service should be issued from
- API URL. This will be pre-populated but should be the URL to the certdog API that will provide the certificates. If certdog is clustered then this may be different to what is automatically populated and should be updated manually
- Auto Generate Credentials. If this is checked (the default), then a new user and team will be created, dedicated for this ACME service. All certificates issued from the service will be associated with this user and team. If this is unchecked then the Certdog Team ID and Certdog User ID fields will be made available and you can enter the values for an existing user and team
- Allow http-01 Challenges. If checked allows the http-01 ACME challenge. Where the client will host a file containing the challenge that the server (certdog) then checks
- Allow dns-01 Challenges. If checked allows the dns-01 ACME challenge. This is where the challenge must be added as a DNS Record for the domain, which the server (certdog) will check
- Terms of Service (Optional). When a client calls the Directory URL, this value will be included in the termsOfService entry within the meta section. Users should confirm that they will adhere to these terms of service
- Website (Optional). When a client calls the Directory URL, this value will be included in the website entry within the meta section
- External Account Binding Required. If this is checked, then clients must be provided with a MAC Key and Key Identifier (KID) and MAC Key before ACME account creation. Clients must provide these details in order to be provided with an ACME account on the server. If this is not checked, then any client (that can reach the Directory URL) will be able to obtain an ACME account. In either case all clients must satisfy the challenges to confirm domain ownership
- Order Expiry (Seconds). When a client places an order, they must satisfy all challenges and collected their certificate within this timeframe
- Authorization Expiry (Seconds). The client must satisfy all challenges included in the authorization within this timeframe
- NONCE Expiry (Seconds). A new NONCE is generated for each call. If the client does not make another call within this timeframe the request for that command will be rejected. If they have the logic, clients can request a new NONCE at this point
- NONCE Bytes. The number of bytes to use for the NONCE. The NONCE is a value that is provided by the server and simply replayed by the client
- Challenge Bytes. The number of bytes to use for the challenge. This is the value that the client must host (for http-01 challenges) or set as a TXT record in their DNS
- Log Protected Section of Payload. The text logs will log every message received and returned. If this is not checked, the protected part of the message will not be logged. The Protected section contains public key data, the account identifier (key ID), algorithm used, URLs and NONCE values. It does not contain any passwords or private keys
- Enforce Strict Payload. According to RFC8555, the payload should be empty for certain requests (such as get-challenge), some ACME clients do not adhere to this (including certbot). If this option is checked it will reject requests that do not contain an empty payload. Leave unchecked for clients that do not strictly adhere to the RFC
Click Add
If all has been created correctly, you should be able to open a Browser and navigate to the Directory URL. You should see JSON returned similar to the following:
{
"keyChange": "https://acme1.certdog.com/certdog/acme/alias1/key-change",
"revokeCert": "https://acme1.certdog.com/certdog/acme/alias1/revoke-cert",
"meta": {
"website": "https://krestfield.com/certdog",
"termsOfService": "https://krestfield.com/acme/tos.pdf"
},
"newNonce": "https://acme1.certdog.com/certdog/acme/alias1/new-nonce",
"newAccount": "https://acme1.certdog.com/certdog/acme/alias1/new-acct",
"newOrder": "https://acme1.certdog.com/certdog/acme/alias1/new-order"
}
Editing a Service
To edit a service, click the service and choose View/Edit:
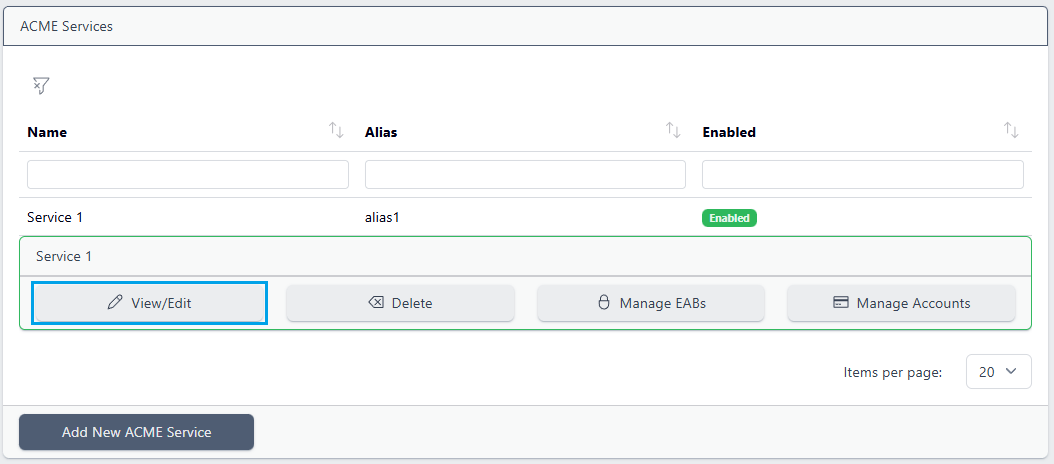
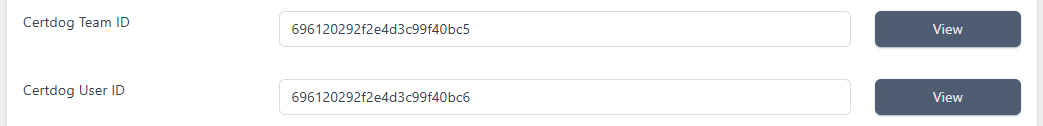
The information previously entered will be displayed and can be edited. Note that if Auto Generate Credentials option was previously set, the created Team and User IDs will now be displayed and can be viewed:
Click Update to save the new settings
Disabling a Service
From the ACME menu, select the service and choose View/Edit
Uncheck the Enabled button
If a client makes a request when the service is disabled the initial request will be rejected with an HTTP Forbidden response, the error message detailing that the service has been disabled
Deleting a Service
From the ACME menu, select the service and choose Delete
Click Yes to confirm
Viewing and Revoking Accounts
To view the ACME accounts that have been created for the service, from the ACME menu, select the service and choose Manage Accounts:
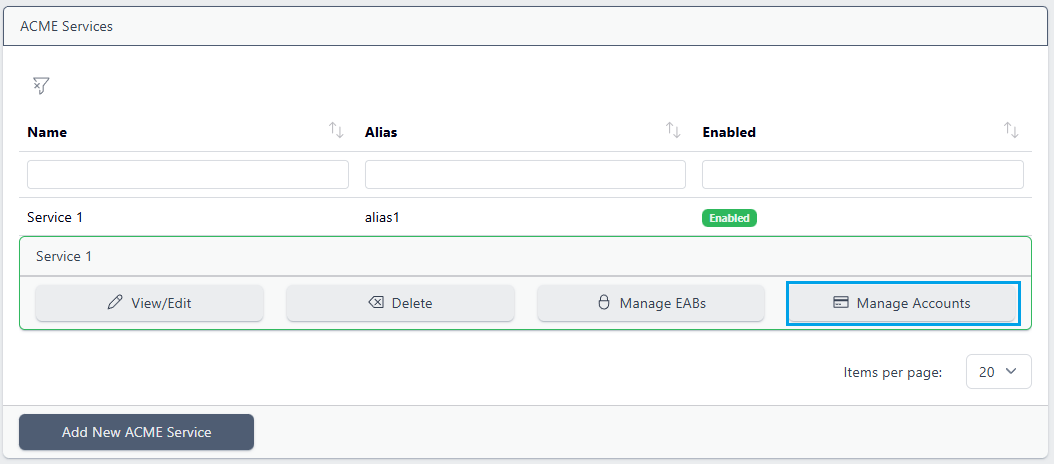
All accounts will be displayed:
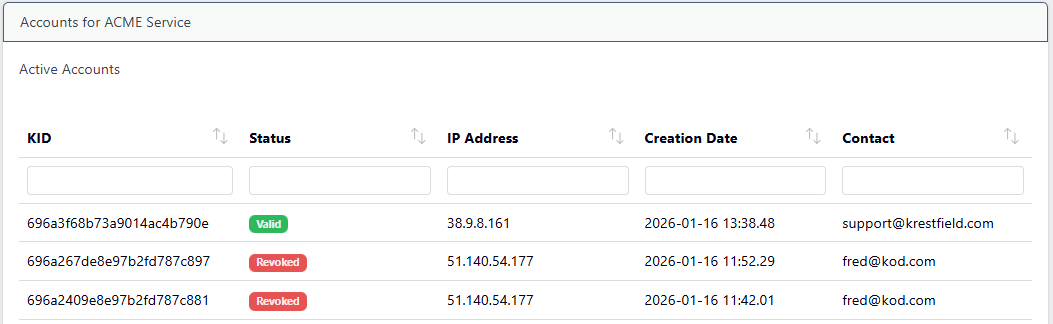
The IP Address indicates the client IP address. The contact details are provided by the user when running the client. If EAB is used, the contact details are extract from the user that the initial EAB key are associated with (see External Account Binding below)
External Account Binding
Use this if you want to pre-authorise clients, assigning the authorisation to an existing certdog user. Note that as an EAB key is associated with a user, the user must be present in certdog. The account can be local, Active Directory or Entra ID based
When EAB is enabled, only clients with a valid Key and Key Identifier will be permitted to create an ACME account on the server. This setting is per service i.e. one ACME service endpoint may require EAB, whilst another may allow auto account creation with no pre-authorisation
Creating an EAB
To enforce, from the ACME menu, select the service you wish to enforce EAB on, and choose View/Edit
Check the External Account Binding Required option and click Update
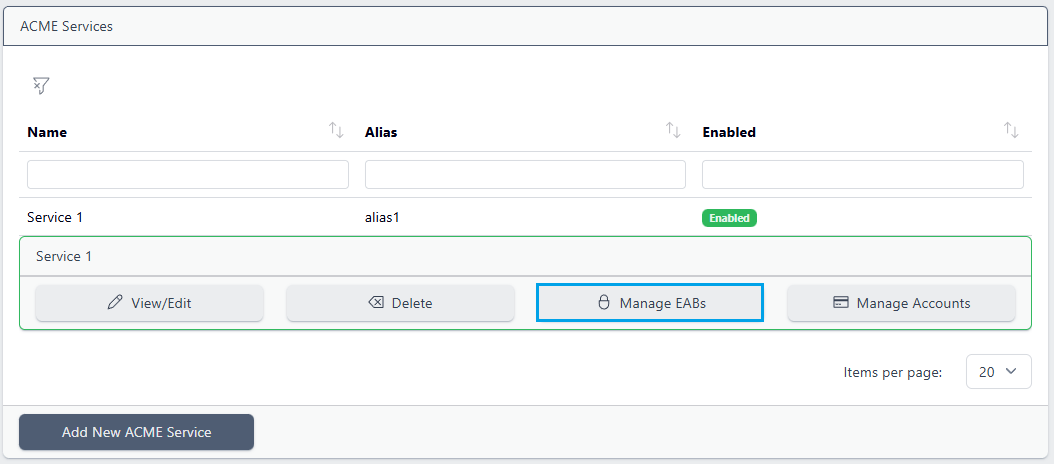
Back on the ACME Services page, click on the same service and choose Manage EABs:
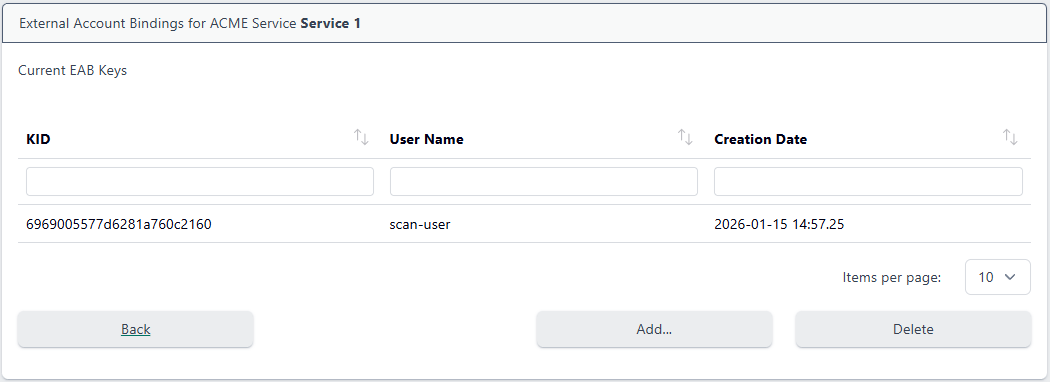
To add a new EAB, click Add…
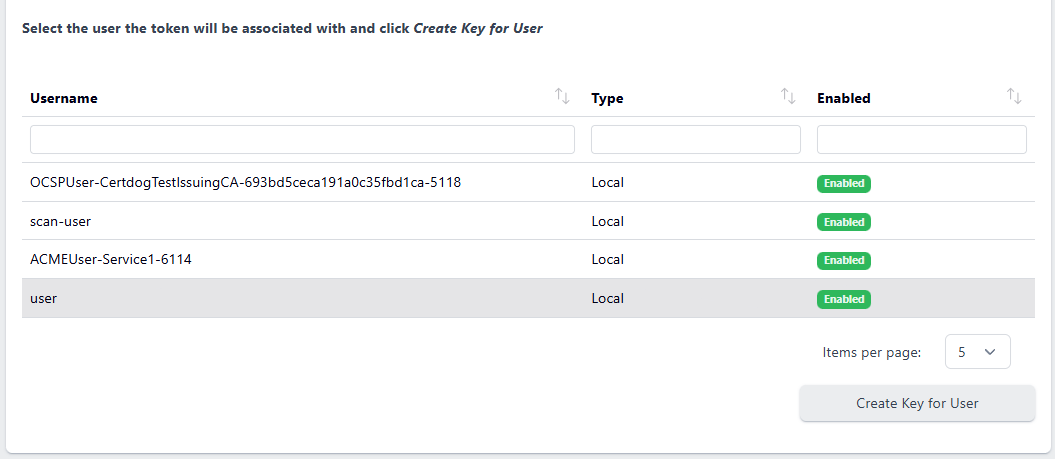
Search for and select the user this key is to be associated with and click Create Key for User:
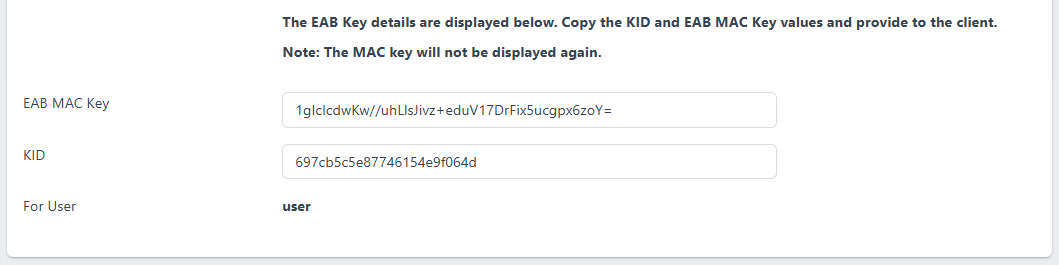
The EAB MAC Key and KID will be displayed. Click to copy the values and securely transport to the user. Note: the EAB MAC Key can not be displayed again. If it is lost then the existing EAB must be deleted and the a new one created
The client will need to supply the EAB MAC Key and KID to their ACME client. The client will then supply these details when requesting an ACME account. Certdog will validate the credentials, also checking that the associated user exists in certdog and is enabled. The client will then be permitted to create an ACME account. Once this has been created it will be used to authenticate to the server from then on
Deleting an EAB
From the ACME Services page, click on the service and choose Manage EABs:

Select the KID to delete and click Delete
Troubleshooting
When using ACME clients such as certbot and win-acme they require that the server end point (the certdog ACME server) is protected with TLS and this certificate is trusted by the client application
If this is not the case, the client will fail to negotiate with the ACME service. You may see errors relating to SSL or certificate validation failures, e.g. certbot may log an error such as:
OpenSSL.SSL.Error: [('SSL routines', 'tls_process_server_certificate', 'certificate verify failed')]
And:
HTTPSConnectionPool(host='certdog.xserver.local', port=443): Max retries exceeded with url: /certdog/acme/alias1/directory (Caused by SSLError(SSLError("bad handshake: Error([('SSL routines', 'tls_process_server_certificate', 'certificate verify failed')])")))
To configure the certdog server with a TLS certificate, follow the steps here
To add the required trust to the ACME client is to ensure that the root certificate from the chain that issued the certdog server TLS certificate is included in the trusted store of the ACME client machine
As an example, trusted certificates can be added to certbot explicitly by obtaining the chain (all CA certificates up to the root) in PEM format and pasting into a text file, in this order:
-- ROOT CA CERTIFICATE --
-- ISSUING CA CERTIFICATE --
For example the file may then look something like:
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----
MIIEFDCCAfygAwIBAgIQKHKRdNhdBzyYWUI9b0HuxjANBgkqhki
...
d/sXZ8iiSfxXHZPV1JI0wAitRZqq4k8TJAJFKzMnrEPEErgki==
-----END CERTIFICATE-----
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----
MIIEFDCCAfygAwIBAH1GfygAwIBAgIQKHKRdNhdjZTIMb2ns+fjN
...
d/sXZ8iiSfxXHZPV1JI0wAitRZqq4AJFKzMnrEPEErgki/eTaA==
-----END CERTIFICATE-----
If this file is named server-trust.pem then the following environment variable can be set before certbot is run:
export REQUESTS_CA_BUNDLE=/home/certbot-app/server-trust.pem
This will add the required trust chain for certbot
But refer to the latest documentation for your ACME client